
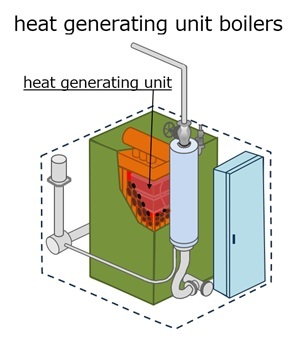
Heat generation unit boiler is a boiler that uses heat from a heat generation unit (Patent No. 5829325 "Heat generation unit and hot water supply system") that combines and operates simultaneously a solid oxide fuel cell (800-1000°C) and a solid oxide electrolysis cell (600-800°C), which have high operating temperatures, to generate heat of 700°C.
Factories can reduce the consumption of hydrogen gas or electricity by replacing fossil fuel boilers and electric boilers with heat generating unit boilers.
Although the heating unit has not yet been commercialized, it can be made using solid oxide fuel cells and solid oxide electrolysis cells manufactured by Magnex Corporation.
The working principle of heat generating unit is as shown in the following video.
As shown in the video, heating unit is integrated by connecting the tube through which hydrogen from the solid oxide fuel cell passes to the tube through which hydrogen from the solid oxide electrolysis cell passes, and by connecting the tube through which oxygen from the solid oxide fuel cell passes to the tube through which oxygen from the solid oxide electrolysis cell passes.
Heat generating unit uses a solid oxide electrolysis cell to produce hydrogen and oxygen from water through electrolysis, and then the solid oxide fuel cell uses this hydrogen and oxygen to produce water and electricity.By repeating this process, continues to generate high operating heat of 700°C.
In order for the heat generating unit to continue generating high operating heat, the amount of electricity supplied to the electrolysis in the solid oxide electrolysis cell is controlled by adding the electricity generated by the solid oxide fuel cell and the amount of electricity from an external power source so that the amount of hydrogen and oxygen is such that the solid oxide fuel cell can generate rated output.
The heating unit is shut down by cutting off the power supply to the solid oxide electrolysis cell.
A heating unit boiler with the same capacity as a 10kW electric boiler can be made using Magnex Co., Ltd.'s G20 (external dimensions: length 150mm x width 150mm x height 135mm) solid oxide electrolysis cells (20 cells) and solid oxide fuel cells (20 cells).
The amount of heat generated by this heating unit is 28,640 J, calculated as follows, assuming that the dimensions of the solid oxide fuel cell and solid oxide electrolysis cell are 11 cm long and 11 cm wide, and the electrolyte is yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which has a thickness of 30 μm, a specific heat of 0.47 kJ/(kg・K), and a bulk density of 6.0 g/cm3.
11cm×11cm×0.003cm×0.47 (specific heat)×6 (specific gravity)×700℃ ≒ 716J
716J×40 cells = 28,640J
A 10kW electric boiler requires 10kW of power consumption while it is running.
When the heat generating unit boilers is started up, it requires a few tens of minutes of heating with a 10 kW electric heater until it reaches the operating temperature. However, once it has reached operating temperature and begun operation, the solid oxide fuel cell generates 725 W and the solid oxide electrolysis cell performs electrolysis at 2.623 kW, meaning that it can continue to operate with an external supply of approximately 2 kW of electricity.
A 10kW electric boiler consumes 10kW of power while in operation, whereas the heat generating unit boilers consumes only 2kW of power, resulting in an energy-saving operation of 8kW.
"Quote":URL of copyrighted work
"Magnex Corporation SOFC/SOEC Stack"
https://www.magnex.co.jp/stack.html